What is a Georeferenced 3D Model?
A georeferenced 3D model is a digital representation of the real world, where the coordinates within the model are tied to actual geographic locations. This means that the model can be used to measure and analyze real-world distances, shapes, and features with high accuracy. By aligning the digital data with a known coordinate system, users can ensure that their 3D models reflect reality at true scale.
When georeferenced, this 3D point cloud provides accurate measurements that match real-world dimensions
These models are incredibly useful for professionals in fields such as engineering, mining, construction, and environmental monitoring. They allow teams to inspect structures, assess damage, and plan projects without physically being on-site. The ability to work with real-world measurements makes them essential tools for accurate decision-making and planning.
The key benefits of using a georeferenced 3D model include:
- Enhanced decision-making through accurate spatial data
- Identification and assessment of structural damage or changes
- Accurate measurement of areas of interest
- Quantification of materials, like stockpile volumes
- Integration and alignment of multiple 3D datasets
How to Create a Georeferenced 3D Model with the Elios 3
The Elios 3 is a specialized drone designed for confined spaces, capable of capturing georeferenced 3D data. It uses a LiDAR scanner to collect millions of points as it flies around an area, creating a detailed point cloud. These point clouds can then be processed into fully georeferenced 3D models, allowing for precise analysis and comparison with real-world measurements.
![2023-09-15 15_02_37-CloudCompare v2.13.alpha (May 16 2023) [64-bit] - [3D View 1]](http://bsg-i.nbxc.com/blog/efd5f8af2ac9b1156df28d3bf37cea0f.png) A point cloud of a carpark showing clear outlines of vehicles
A point cloud of a carpark showing clear outlines of vehicles
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Site Preparation
Before starting, ensure the site is safe for flight. Remove any hazards such as water, cables, or obstacles. Place retroreflective targets around the area you will scan. These targets help the software align the data with real-world coordinates. At least four targets should be placed at different heights and positions to ensure accurate georeferencing.
Step 2: Georeferencing the Targets
Use a total station to record the exact coordinates of each target. This data is then exported as a CSV file and used during processing. Proper placement and recording of these targets are crucial for ensuring the final 3D model reflects real-world measurements accurately.
A surveyor setting up retroreflective targets for georeferencing
Step 3: Taking Flight
Fly the Elios 3 in mapping mode with assist enabled. Perform a 360-degree rotation over the take-off area before moving forward. Pass each target at a distance of 1–3 meters and perform another 360-degree rotation. Keep the flight smooth and avoid sudden movements to ensure accurate data collection.
An example flight path with 360-degree rotations around targets
After completing the scan, return the drone to the take-off point and perform one last 360-degree spin before landing. This helps close the loop and ensures the data is properly aligned during processing.
Step 4: Processing the Data
Export the data from FlyAware and import it into FARO Connect. Use the Flyability processing template and select the environment type (e.g., tunnels, confined spaces). During registration, input the coordinates of the retroreflective targets to help the software georeference the entire model accurately.
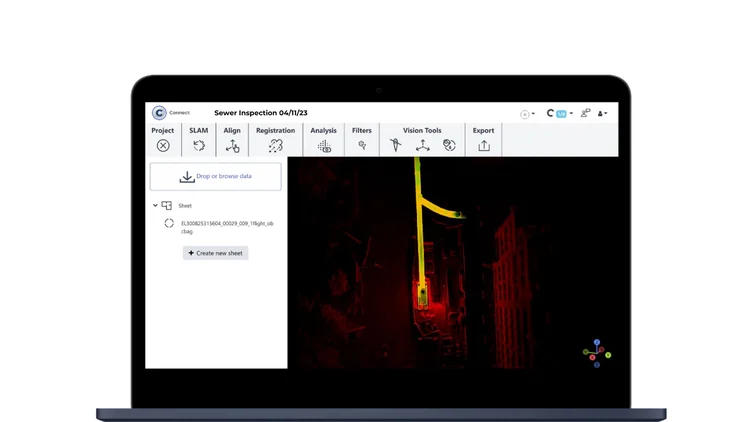 FARO Connect is optimized for processing data from the Elios 3
FARO Connect is optimized for processing data from the Elios 3
Once registered, the software will automatically align and georeference the point cloud. Follow Flyability’s training materials to generate high-quality, georeferenced *.las files suitable for further analysis and use in CAD or GIS systems.
What's Next: Uses for 3D Models
Once your model is georeferenced, you can use it for detailed analysis or export it as a .las file. These files can be imported into CAD software or other platforms that support georeferenced data. This makes them ideal for asset management, maintenance planning, and infrastructure design.
Two point clouds merged using common targets for accurate alignment
Georeferenced 3D models are widely used across industries such as mining, construction, and utilities. Examples include improving sewer inspections, identifying blockages in orepasses, and measuring stockpile volumes. These models provide valuable insights and help teams make informed decisions efficiently.
With the right tools and techniques, you can create accurate, georeferenced 3D models using the Elios 3 and FARO Connect. For more information or to access training resources, visit Flyability’s website and connect with their team for guidance on advanced data processing and georeferencing best practices.
Custom Stickers,Personalised Stickers,Vistaprint Stickers,Custom Floor Sticker
Jiangmen Yingzhihui Electronic Commerce Co., LTD , https://www.yzhprint.com